 |
|
 |
|
The mean molar mass of air is 28.97 g/mol.
http://www.physlink.com/education/askexperts/ae650.cfm What is the weight of 1 cubic foot of air?
standard temperature and pressure (STP)
FINAL ANSWER: 1 cubic foot of air (STP) assuming average composition weighs approximately 0.0807 lbs.
1 pound = 453.59237 grams
1 cubic foot of air at standard temperature and pressure = 36.604904 grams
1 cubic foot is .02831685 cubic metters
1 cubic meter of air at standard temperature and pressure = 1292.8294 grams
1 cubic inch of air at standard temperature and pressure = 0.021183394 grams
How does one compare the amount of CO2 and H20. CO2 is expressed in ppm
1 gram of water per cubic foot is 27322 ppm.


How does CO2 at 385 PPM with H20 in PPM by the natural dew point defined for air.
There is a neat property that applies to any gas that a 22.4 liters of it at STP contains 6.02214199 x10^23 molecules of said gas.
28.32 liters of gas at STP is going to be 1.26414494 moles of air.
6.02214199 x10^23 times 1.26414494 is the number of molecules in 1 cubic foot of air.
7.6128603 x10^23 times is the number of molecules in 1 cubic foot of air.
0.004.4055905 x10^20 is the number of molecules in 1 cubic inch of air.
NTP - Normal Temperature and Pressure - is defined as air at 20oC (293.15 K, 68oF) and 1 atm ( 101.325 kN/m2, 101.325 kPa, 14.7 psia, 0 psig, 30 in Hg, 760 torr)
Saturated Water Vapor Pressure in mb es per degree C.
Bolton 1980 within 0.3% for -35C to 35 C =EXP(17.67*C10/(C10+243.5))*6.112 C10 is a temp C cell.
Goff, J. A., and S. Gratch (1946) Low-pressure properties of water from -160 to 212 °F http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Water_vapor
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Goff-Gratch_equation
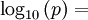 |  |
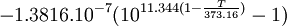 | |
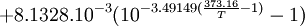 | |
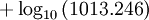 | |
Open Office oocalc function expressing above equation.
=POWER(10;-7.90298*(373.16/A10-1)+5.02808*LOG(373.16/A10;10)-1.3816*POWER(10;-7)*POWER(10;11.344*(1-A10/373.16)-1)+8.1328*POWER(10;-3)*(POWER(10;-3.49149*(373.16/A10-1))-1)+LOG(1013.246;10))
p units hPA, T Units Kelvin A10 is cell holding temp in K.
PV=nRT Pressure * Volume = Moles * gas constant * Temp K
n/V = P/RT Moles / Volume = Pressure/( gas constant * Temp K )
units of gas constant R Pa m3 K-1 moles-1
n=PV/RT
moles are an avargardo number of molecules.
moist air = moles of dry air + moles of h20
PPM of h20 = moles of h20 / moles of dry air * 106
What volume contains 1 million molecules? 1.313566e-16 cubic feet.
What is the length of a side of that cube? The cube root of 1.313566e-16 is 0.000005083357257494382 feet is 1.549407292 microns or .06001 thousandths of an inch.
Human hair is reported to have diameters that vary from 17 to 181 microns. http://hypertextbook.com/facts/1999/BrianLey.shtml
So a cube with dimensions 1/10th to 1/100th the thickness of a hair has 336 or whatever ppm of CO2.
6.02214199 x10^23 times Carbon Dioxide (CO2): 0.0003792 moles = 2.2835962x10^20 CO2 molecules per cubic foot.
228,359,620,000,000,000,000 That's 228.35962 million billion molecules of CO2 per cubic foot.
132,152,560,000,000,000 or 132,152.56 billion molecules of CO2 per cubic in.
At 384 PPM CO2, For every molecule of C02 in the air there are about 2598 molecules of other gasses.
Oxygen: 20.99% 546
Nitrogen: 78.03% 2032
Carbon Dioxide: 0.03% 1
Hydrogen: 0.00005% .00000015
Argon: 0.93% 24
Neon: 0.0018%
Helium: 0.0005% 1.6
Krypton: 0.0001% .00333
Xenon: 0.000009% .0003
Water Vapor .25 to 3% 7.5 to 90
1 year = 31 556 926 seconds
Earth\ufffds radius (6.37 106 m) radius of Earth = 6 378 100 meters
The area of earth disc is equal to pr2 1.278004e+14 meters^2
Earth-Sun distance, 1.5x10^11 meters.
Energy reaches the surface of such a sphere at a rate of 1370 W/m^2.
Annual energy reaching earth in Joules.
A Watt is a joule per second.
1370 W/m^2 TIMES 31,556,926seconds/year TIMES 1.278004 X10^14 m^2 = 5.525197 X10e24 joules/year
in a gram of water there are 3.34x10^22 molecules of h20.
1 eV is approximately 1.602 × 10-19 joules
1 cubic meter = 35.3146667 cubic foot
Ideal gas law PV =nRT
From the ideal gas law key concepts to simplify understanding air or an uncontained volume are this.
In a given volume the pressure of a gas is a function of the number of molecules in that volume.
The number of molecules in a volume at a given pressure is a function of the temperature.
The weight of a given volume is a function of the sum of the masses of all molecules within.
The weight of a given volume is also it's density.
The density of a given volume is a function of sum of the masses of it's mix of different molecules.
E=hc/wavelength
http://www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/quantumzone/photoelectric2.html Planck's Constant and the Energy of a Photon
http://www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/microwaves/images/molSpark.gif
http://www.climateaudit.org/?p=2572 Tuesday, January 8th, 2008 at 2:27 pm
Sir John Houghton on the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect By Steve McIntyre
Planck's Constant can also be expressed as approximately 6.626 × 10-34 joule·seconds or 4.135 × 10-15 eV·seconds.